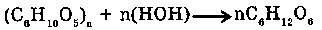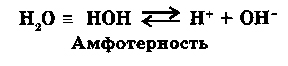
Water is an ideal amphoteric combination, as it formes equal number of ions H+ and OH-.
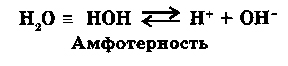
1. ACID PROPERTIES OF WATER:
With Na, K and Ca water reacts at usual temperature; with Mg - at boiling.
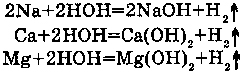
2. WITH AMPHOTERIC METALS:
With Zn the reaction goes during boiling; with Al, if it is without oxid cover as solution in Rt - at usual temperature; with Fe - at high temperature.
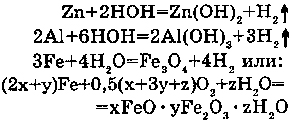
3. WITH THE OXIDS OF ACTIVE METALS:
For example, with CaO (oxids of all metals in a line of voltage up to Mg inclusive).
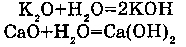
4. WITH AMMONIA:
Water is the donor of a proton, under the theory of Laury - Bernstad it is an acid. Therefore, it is capable to react with ammonia, as an acid, with formation of the cation of ammonia.
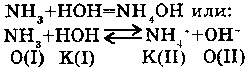
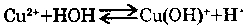
5. HYDROLYSIS OF THE SALTS:
Salt formed by the weak bases, are hydrolysed by water. For example, with CuCl2 hydrolysis goes in steps.
 (1rst step)
(1rst step)
1. WITH ACID OXIDS: For example, reaction of water with SO3 makes H2SO4
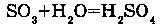
2. WITH ACIDS:
In this case water is an acceptor of a proton, under the theory of Laura - Bernstad it is the basis.
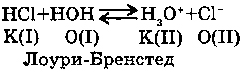
3. HYDROLYSIS OF THE SALTS:
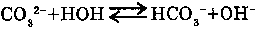
Salt formed by weak acids, are hydrolysed by water. For the multibasic acids the reaction goes in steps.
 (1rst step)
(1rst step)
The atom of oxygen has in water a degree of oxidation -2, and that causes properties of water as a recoveror.
1. With F2, Cl2:
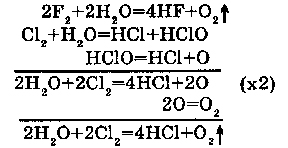
2. DECOMPOSITION:
Electrolysis is the reaction of intomolecular oxidation - restoration.
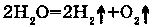
3. WITH MOLECULAR OXYGEN:
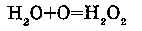
1. WITH THE SULFURIC ACID (H2SO4):
With a sulfuric acid water forms hydrates.
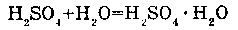
2. WITH SALTS:
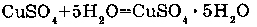
3. WITH GASES
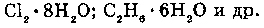
1. WITH ALKENS (CnH2n) (adjoining):
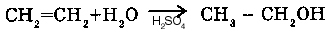
2. WITH ALKENS (CnH2n) (oxydation):
Reaction of Wagner
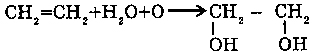
3. WITH ALKINS (CnH2n-2):
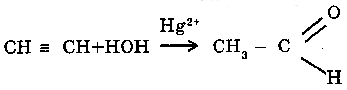
O
5. WITH COMPLEX ETHERS (čR- C -O-R):
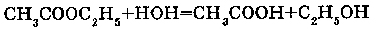
6. WITH CaC2:
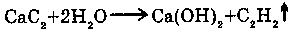
7. WITH POLYSACCHARIN: